Braun Lab
Ion transport mechanisms in megakaryocytes and platelets
Ion transport mechanisms in megakaryocytes and platelets

Role of channels in Ca2+ homeostasis in
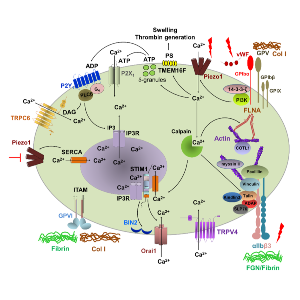
Blood flow-induced hemodynamic changes result in mechanical stress on blood cells and vessel walls. Increased shear stress can activate platelets and other circulating cells, triggering the rapid activation of receptors, calcium channels, and related signaling mechanisms. Shear stress can also modify the folding of extracellular molecules and directly activate mechanosensitive receptors and calcium channels. The mechanical movement of the extracellular matrix and the intracellular cortical actin cytoskeleton can change the conformation of platelet receptors and gate channel pores in the plasma membrane. Mechanosensitive platelet receptors and their downstream signaling events and metabolic products can also indirectly activate calcium channels. While the molecular composite of mechanotransduction pathways has been described in mammals, shear stress-induced platelet receptors and their crosstalk with calcium channels have been incompletely characterized. Therefore we are investigating the role of mechano-sensitive platelet receptors and calcium channels upon platelet activation and different disease contexts such as arterial thrombus formation.
Proposed model of mechanotransduction in blood platelets. Shear-dependent activation of GPIbα receptor modulates mechano-signal with PI3-kinase to Piezo1. Mechanical membrane stretch opens the channel pore of Piezo1 and subsequent Ca2+ influx enhances degranulation and calpain activities. Piezo1-mediated Ca2+ influx stimulates purinergic responses through granule secretion and subsequent ATP/ADP release, and also activates TMEM16F-mediated PS exposure. TMEM16F-induced platelet swelling further enhances Piezo1 activity. Calpain cleaves talin and other members of actin cytoskeleton, thereby activating αIIbβ3 integrins, and modulating myosin II and COTL1 functions. Calpain cleaves STIM1 and other components of SOCE complex thereby regulating ORAI1 activity. Piezo1 activity is probably downregulated by SERCA translocation to the plasma membrane during SOCE. The roles of GPVI and TRPV4 in platelet mechanotransduction have not been elucidated, probably activated by GPIbα and αIIbβ3 integrin, respectively.
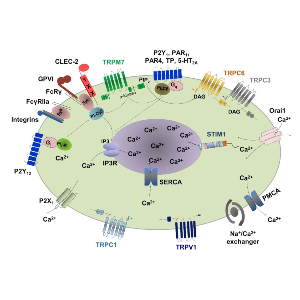
Platelet receptor-induced phospholipase C activation and consequent hydrolysis of PIP2 to IP3 and DAG is a central event to modulate Ca2+ responses during platelet activation. Elevation of the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration occurs through Ca2+ release from the IP3 sensitive intracellular Ca2+ stores located in the dense tubular system (DTS). Calcium-store depletion and increase of DAG production induce Ca2+ entry mechanisms through store-operated Ca2+ channels (SOC) and DAG sensitive receptor-operated Ca2+ channels (ROC), respectively. During the last decade, our research group is strongly focused to understand the molecular mechanism of SOCE and ROCE using platelets isolated from genetically modified mice. We identified the physiological role of the Ca2+ sensor stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) and Ca2+ channel ORAI1 as the principal mediators of SOCE in platelets. Our findings also revealed that TRPC6 is the major DAG-sensitive ROC channel in platelets. Under pathophysiological conditions, we could identify STIM1 and ORAI1 isoforms as an important player in arterial thrombus formation and contributes to stroke development in vivo. Interestingly, STIM2 and ORAI2 functions were found to be redundant in platelets, but importantly, regulates neuronal SOCE in the mouse brain. Using knockout mouse models of different channelopathies, we further study Ca2+ entry mechanisms and their signaling pathways in different pathophysiological conditions in vivo Role of channels in Ca2+ homeostasis in platelets. Upon platelet activation, the majority of platelet-activating receptors (P2Y1, P2Y12, PAR1, PAR4, TP, 5-HT2A, GPVI, CLEC-2, P2Y12) act through the stimulation of phospholipase C (PLC) β and γ isoforms, which catalyze the hydrolysis of phosphatidyl 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3). IP3 releases Ca2+ from the intracellular stores and STIM1 polymerization opens Orai1 channels in the plasma membrane, a process called store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE). In contrast, receptor-operated Ca2+ entry (ROCE) is regulated mainly by ATP and DAG. TRPC6 channel is the main regulator of DAG-mediated ROCE. ATP-activated P2X1 Ca2+ permeable channel and Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) contribute to the increase of intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i). Ca2+ can be pumped back into the stores or through the plasma membrane to the outside of platelets by SERCA and PMCA Ca2+ ATPases. Platelets express a constitutively active Mg2+ and Ca2+ permeable channel TRPM7. The kinase domain of this channel also activates PLC signaling and induces SOCE in platelets.

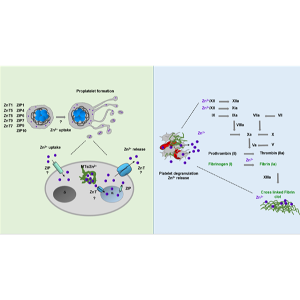
Predicted role of zinc transporters in megakaryocytes/platelets and blood clot formation.
Although it has been known for more than 50 years that reduced Mg2+ uptake frequently induces imbalanced Ca2+ responses in mammalian cells, the molecular players behind this process have not been identified. Impaired Mg2+ homeostasis is described in many cardiovascular diseases, especially in patients with coronary heart disease, arrhythmia, acute myocardial infarction, hypertension and stroke. We could identify TRPM7 channel as a key regulator of Mg2+ homeostasis in mouse megakaryocytes. Impaired channel activity of TRPM7 resulted in macrothrombocytopenia in mice and human patients, associated with abnormal myosin IIa function and platelet production. On the other hand, we found that the kinase domain of TRPM7 modulates Ca2+ store depletion and activates SOCE during platelet activation, suggesting that TRPM7, depending on the physiological status of the cell, can regulate both Mg2+ and Ca2+ homeostasis in these cells. We further investigate TRPM7 mediated signalling in megakaryocytes and platelets.
Other important nutrition, zinc (Zn2+) also circulates in the blood plasma, but only small amounts are present as a free metabolic form, which can be taken up by platelets and other blood cells. Reduced Zn2+ uptake in the body results in altered platelet aggregation responses and impaired hemostasis, while intracellular chelation of Zn2+ in platelets inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation cascades, platelet reactivity and aggregation responses. Earlier findings showed that incubation platelets with Zn2+ supplement increases intracellular Zn2+ level and also in the granules, pointing to the existence of Zn2+ uptake and storage mechanisms, although the molecular mechanism of Zn2+ transport and storage are still unknown in megakaryocytes and platelets. Furthermore, the Zn2+ concentration in blood serum was found to be higher than in plasma, suggesting that activated platelets can release a significant amount of stored Zn2+ during blood clotting. To study these processes, we isolated platelets from mouse models of storage pool disorders (SPD) and found abnormal storage and release of Zn2+ and these abnormalities were confirmed in human SPD patients as well. Impaired Zn2+ release could negatively influence fibrin formation, therefore we concluded that secretory granule resident of Zn2+ contributes to blood clotting. We identified several Zn2+ transporters in megakaryocytes and platelets which may be involved in diverse signaling functions of these cell types. Using different knockout and knockin cells and platelets, we are investigating Zn2+ dependent pathological processes in mice and humans.
| Name | Tel | Room | Position | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Klepsler, Iona | iona.klepser@campus.lmu.de | Doctoral student | ||
| Manieri, Mara | Mara.Manieri@campus.lmu.de | Doctoral student |
1. Braun A, Mammadova-Bach E. GALE force in platelet production. Blood. 2023 Jan. 26;141(4):330-331.
2. Yang L, Steiger S, Shi C, Gudermann T, Mammadova-Bach E, Braun A, Anders HJ. Both hyperglycemia and hyperuricemia aggravate acute kidney injury during cholesterol embolism syndrome despite opposite effects on kidney infarct size. Kidney Int. 2023 Jul;104(1):139-150.
3. Gotru SK, Mammadova-Bach E, Sogkas G, Schuhmann MK, Schmitt K, Kraft P, Herterich S, Mamtimin M, Pinarci A, Beck S, Stritt S, Han C, Ren P, Freund JN, Klemann C, Ringshausen FC, Heemskerk JWM, Dietrich A, Nieswandt B, Stoll G, Gudermann T, Braun A. MAGT1 Deficiency Dysregulates Platelet Cation Homeostasis and Accelerates Arterial Thrombosis and Ischemic Stroke in Mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023 Aug;43(8):1494-1509.
4. Han C, Ren P, Mamtimin M, Kruk L, Sarukhanyan E, Li C, Anders HJ, Dandekar T, Krueger I, Elvers M, Goebel S, Adler K, Münch G, Gudermann T, Braun A, Mammadova-Bach E. Minimal Collagen-Binding Epitope of Glycoprotein VI in Human and Mouse Platelets. Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 1;11(2):423.
5. Mammadova-Bach E, Gudermann T, Braun A. Platelet Mechanotransduction: Regulatory Cross Talk Between Mechanosensitive Receptors and Calcium Channels. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023 Aug;43(8):1339-1348.
6. Kruk L, Braun A, Cosset E, Gudermann T, Mammadova-Bach E. Galectin functions in cancer-associated inflammation and thrombosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 17;10:1052959.
7. Kruk L, Mamtimin M, Braun A, Anders HJ, Andrassy J, Gudermann T, Mammadova-Bach E. Inflammatory Networks in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 9;15(8):2212. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082212.
8. Mamtimin M, Pinarci A, Han C, Braun A, Anders HJ, Gudermann T, Mammadova-Bach E. Extracellular DNA Traps: Origin, Function and Implications for Anti-Cancer Therapies. Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 27;12:869706.
9. Kazandzhieva K, Mammadova-Bach E, Dietrich A, Gudermann T, Braun A. TRP channel function in platelets and megakaryocytes: basic mechanisms and pathophysiological impact. Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Sep;237:108164.
10. Braun A, Anders HJ, Gudermann T, Mammadova-Bach E. Platelet-Cancer Interplay: Molecular Mechanisms and New Therapeutic Avenues. Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 12;11:665534.
11. Mammadova-Bach E, Braun A. Platelet life without TMEM163: no dense granules. Blood. 2021 Apr 1;137(13):1708-1709.
12. Balkenhol J, Kaltdorf KV, Mammadova-Bach E, Braun A, Nieswandt B, Dittrich M, Dandekar T. Comparison of the central human and mouse platelet signaling cascade by systems biological analysis. BMC Genomics. 2020 Dec 22;21(1):897.
13. Shi C, Yang L, Braun A, Anders HJ. Extracellular DNA-A Danger Signal Triggering Immunothrombosis. Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 7;11:568513.
14. Mammadova-Bach E, Jaeken J, Gudermann T, Braun A. Platelets and Defective N-Glycosylation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 6;21(16):5630.
15. Volz J, Kusch C, Beck S, Popp M, Vögtle T, Meub M, Scheller I, Heil HS, Preu J, Schuhmann MK, Hemmen K, Premsler T, Sickmann A, Heinze KG, Stegner D, Stoll G, Braun A, Sauer M, Nieswandt B. BIN2 orchestrates platelet calcium signaling in thrombosis and thrombo-inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2020 Nov 2;130(11):6064-6079.
16. Shi C, Kim T, Steiger S, Mulay SR, Klinkhammer BM, Bäuerle T, Melica ME, Romagnani P, Möckel D, Baues M, Yang L, Brouns SLN, Heemskerk JWM, Braun A, Lammers T, Boor P, Anders HJ. Crystal Clots as Therapeutic Target in Cholesterol Crystal Embolism. Circ Res. 2020 Apr 10;126(8):e37-e52.
17. Mammadova-Bach E, Gil-Pulido J, Sarukhanyan E, Burkard P, Shityakov S, Schonhart C, Stegner D, Remer K, Nurden P, Nurden AT, Dandekar T, Nehez L, Dank M, Braun A, Mezzano D, Abrams SI, Nieswandt B. Platelet glycoprotein VI promotes metastasis through interaction with cancer cell-derived galectin-3. Blood. 2020 Apr 2;135(14):1146-1160.
18. Mammadova-Bach E, Braun A. Zinc Homeostasis in Platelet-Related Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 23;20(21):5258.
19. Scheller I, Stritt S, Beck S, Peng B, Pleines I, Heinze KG, Braun A, Otto O, Ahrends R, Sickmann A, Bender M, Nieswandt B. Coactosin-like 1 integrates signaling critical for shear-dependent thrombus formation in mouse platelets. Haematologica. 2020 Jun;105(6):1667-1676.
20. Stegner D, Hofmann S, Schuhmann MK, Kraft P, Herrmann AM, Popp S, Höhn M, Popp M, Klaus V, Post A, Kleinschnitz C, Braun A, Meuth SG, Lesch KP, Stoll G, Kraft R, Nieswandt B. Loss of Orai2 Mediated Capacitative Calcium Entry Is Neuroprotective in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke. 2019 Nov;50(11):3238-3245.
21. Nagy M, van Geffen JP, Stegner D, Adams DJ, Braun A, de Witt SM, Elvers M, Geer MJ, Kuijpers MJE, Kunzelmann K, Mori J, Oury C, Pircher J, Pleines I, Poole AW, Senis YA, Verdoold R, Weber C, Nieswandt B, Heemskerk JWM, Baaten CCFMJ. Comparative Analysis of Microfluidics Thrombus Formation in Multiple Genetically Modified Mice: Link to Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019 Jul 30;6:99.
22. Kiran Gotru S, van Geffen JP, Nagy M, Mammadova-Bach E, Eilenberger J, Volz J, Manukjan G, Schulze H, Wagner L, Eber S, Schambeck C, Deppermann C, Brouns S, Nurden P, Greinacher A, Sachs U, Nieswandt B, Hermanns HM, Heemskerk JWM, Braun A. Defective Zinc homeostasis in mouse and human platelets with α- and δ-storage pool diseases. Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 6;9(1):8333.
23. Neidler S, Kruspig B, Hewit K, Monteverde T, Gyuraszova K, Braun A, Clark W, James D, Hedley A, Nieswandt B, Shanks E, Dick C, Murphy DJ. Identification of a Clinically Relevant Signature for Early Progression in KRAS-Driven Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Apr 29;11(5):600.
24. Mittermeier L, Demirkhanyan L, Stadlbauer B, Breit A, Recordati C, Hilgendorff A, Matsushita M, Braun A, Simmons DG, Zakharian E, Gudermann T, Chubanov V. TRPM7 is the central gatekeeper of intestinal mineral absorption essential for postnatal survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 1. 5;116(10):4706-4715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1810633116.
25. Tseng YL, Braun A, Chang JP, Chiang ML, Tseng CY, Chen W. Micromolar concentrations of citalopram or escitalopram inhibit glycoprotein VI-mediated and integrin αIIbβ3-mediated signaling in human platelets. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 1;364:106-113.
26. Mammadova-Bach E, Nagy M, Heemskerk JWM, Nieswandt B, Braun A. Store-operated calcium entry in thrombosis and thrombo-inflammation. Cell Calcium. 2019 Jan;77:39-48.
27. Mammadova-Bach E, Mauler M, Braun A, Duerschmied D. Autocrine and paracrine regulatory functions of platelet serotonin. Platelets. 2018 Sep;29(6):541-548.
28. Stritt S, Birkholz I, Beck S, Sorrentino S, Sapra KT, Viaud J, Heck J, Gaits-Iacovoni F, Schulze H, Du X, Hartwig JH, Braun A, Bender M, Medalia O, Nieswandt B. Profilin 1-mediated cytoskeletal rearrangements regulate integrin function in mouse platelets. Blood Adv. 2018 May 8;2(9):1040-1045.
29. Gotru SK, Gil-Pulido J, Beyersdorf N, Diefenbach A, Becker IC, Vögtle T, Remer K, Chubanov V, Gudermann T, Hermanns HM, Nieswandt B, Kerkau T, Zernecke A, Braun A. Cutting Edge: Imbalanced Cation Homeostasis in MAGT1-Deficient B Cells Dysregulates B Cell Development and Signaling in Mice. J Immunol. 2018 Apr 15;200(8):2529-2534.
30. Nagy M, Mastenbroek TG, Mattheij NJA, de Witt S, Clemetson KJ, Kirschner J, Schulz AS, Vraetz T, Speckmann C, Braun A, Cosemans JMEM, Zieger B, Heemskerk JWM. Variable impairment of platelet functions in patients with severe, genetically linked immune deficiencies. Haematologica. 2018 Mar;103(3):540-549.
31. Gotru SK, Chen W, Kraft P, Becker IC, Wolf K, Stritt S, Zierler S, Hermanns HM, Rao D, Perraud AL, Schmitz C, Zahedi RP, Noy PJ, Tomlinson MG, Dandekar T, Matsushita M, Chubanov V, Gudermann T, Stoll G, Nieswandt B, Braun A. TRPM7 Kinase Controls Calcium Responses in Arterial Thrombosis and Stroke in Mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Feb;38(2):344-352.
32. Stritt S, Beck S, Becker IC, Vögtle T, Hakala M, Heinze KG, Du X, Bender M, Braun A, Lappalainen P, Nieswandt B. Twinfilin 2a regulates platelet reactivity and turnover in mice. Blood. 2017 Oct 12;130(15):1746-1756.
33. Chubanov V, Ferioli S, Wisnowsky A, Simmons DG, Leitzinger C, Einer C, Jonas W, Shymkiv Y, Bartsch H, Braun A, Akdogan B, Mittermeier L, Sytik L, Torben F, Jurinovic V, van der Vorst EP, Weber C, Yildirim ÖA, Sotlar K, Schürmann A, Zierler S, Zischka H, Ryazanov AG, Gudermann T. Epithelial magnesium transport by TRPM6 is essential for prenatal development and adult survival. Elife. 2016 2. Dec 19;5:e20914.
34. Baig AA, Haining EJ, Geuss E, Beck S, Swieringa F, Wanitchakool P, Schuhmann MK, Stegner D, Kunzelmann K, Kleinschnitz C, Heemskerk JW, Braun A, Nieswandt B. TMEM16F-Mediated Platelet Membrane Phospholipid Scrambling Is Critical for Hemostasis and Thrombosis but not Thromboinflammation in Mice-Brief Report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Nov;36(11):2152-2157.
35. Regn M, Laggerbauer B, Jentzsch C, Ramanujam D, Ahles A, Sichler S, Calzada- Wack J, Koenen RR, Braun A, Nieswandt B, Engelhardt S. Peptidase inhibitor 16 is a membrane-tethered regulator of chemerin processing in the myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Oct;99:57-64.
36. Stritt S, Nurden P, Favier R, Favier M, Ferioli S, Gotru SK, van Eeuwijk JM, Schulze H, Nurden AT, Lambert MP, Turro E, Burger-Stritt S, Matsushita M, Mittermeier L, Ballerini P, Zierler S, Laffan MA, Chubanov V, Gudermann T, Nieswandt B, Braun A. Defects in TRPM7 channel function deregulate thrombopoiesis through altered cellular Mg(2+) homeostasis and cytoskeletal architecture. Nat Commun. 2016 Mar 29;7:11097. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11097.
37. Wolf K, Braun A, Haining EJ, Tseng YL, Kraft P, Schuhmann MK, Gotru SK, Chen W, Hermanns HM, Stoll G, Lesch KP, Nieswandt B. Partially Defective Store Operated Calcium Entry and Hem(ITAM) Signaling in Platelets of Serotonin Transporter Deficient Mice. PLoS One. 2016 Jan 22;11(1):e0147664.
38. Mattheij NJ, Braun A, van Kruchten R, Castoldi E, Pircher J, Baaten CC, Wülling M, Kuijpers MJ, Köhler R, Poole AW, Schreiber R, Vortkamp A, Collins PW, Nieswandt B, Kunzelmann K, Cosemans JM, Heemskerk JW. Survival protein anoctamin-6 controls multiple platelet responses including phospholipid scrambling, swelling, and protein cleavage. FASEB J. 2016 Feb;30(2):727-37.
39. Hofmann S, Braun A, Pozgaj R, Morowski M, Vögtle T, Nieswandt B. Mice lacking the SLAM family member CD84 display unaltered platelet function in hemostasis and thrombosis. PLoS One. 2014 Dec 31;9(12):e115306.
40. Göbel K, Schuhmann MK, Pankratz S, Stegner D, Herrmann AM, Braun A, Breuer J, Bittner S, Ruck T, Wiendl H, Kleinschnitz C, Nieswandt B, Meuth SG. Phospholipase D1 mediates lymphocyte adhesion and migration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 2014 Aug;44(8):2295-305.
41. Montani L, Buerki-Thurnherr T, de Faria JP, Pereira JA, Dias NG, Fernandes R, Gonçalves AF, Braun A, Benninger Y, Böttcher RT, Costell M, Nave KA, Franklin RJ, Meijer D, Suter U, Relvas JB. Profilin 1 is required for peripheral nervous system myelination. Development. 2014 Apr;141(7):1553-61.
42. Timofeev O, Schlereth K, Wanzel M, Braun A, Nieswandt B, Pagenstecher A, Rosenwald A, Elsässer HP, Stiewe T. p53 DNA binding cooperativity is essential for apoptosis and tumor suppression in vivo. Cell Rep. 2013 May 30;3(5):1512-25.
43. Pfeiffer V, Götz R, Xiang C, Camarero G, Braun A, Zhang Y, Blum R, Heinsen H, Nieswandt B, Rapp UR. Ablation of BRaf impairs neuronal differentiation in the postnatal hippocampus and cerebellum. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58259.
44. Bender M, May F, Lorenz V, Thielmann I, Hagedorn I, Finney BA, Vögtle T, Remer K, Braun A, Bösl M, Watson SP, Nieswandt B. Combined in vivo depletion of glycoprotein VI and C-type lectin-like receptor 2 severely compromises hemostasis and abrogates arterial thrombosis in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 May;33(5):926-34.
45. Gupta S, Braun A, Morowski M, Premsler T, Bender M, Nagy Z, Sickmann A, Hermanns HM, Bösl M, Nieswandt B. CLP36 is a negative regulator of glycoprotein VI signaling in platelets. Circ Res. 2012 Nov 9;111(11):1410-20.
46. van Kruchten R, Braun A, Feijge MA, Kuijpers MJ, Rivera-Galdos R, Kraft P, Stoll G, Kleinschnitz C, Bevers EM, Nieswandt B, Heemskerk JW. Antithrombotic potential of blockers of store-operated calcium channels in platelets. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Jul;32(7):1717-23.
47. Nevalainen EM, Braun A, Vartiainen MK, Serlachius M, Andersson LC, Moser M, Lappalainen P. Twinfilin-2a is dispensable for mouse development. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22894.
48. Hulot JS, Fauconnier J, Ramanujam D, Chaanine A, Aubart F, Sassi Y, Merkle S, Cazorla O, Ouillé A, Dupuis M, Hadri L, Jeong D, Mühlstedt S, Schmitt J, Braun A, Bénard L, Saliba Y, Laggerbauer B, Nieswandt B, Lacampagne A, Hajjar RJ, Lompré AM, Engelhardt S. Critical role for stromal interaction molecule 1 in cardiac hypertrophy. Circulation. 2011 Aug 16;124(7):796-805.
49. Braun A, Vogtle T, Varga-Szabo D, Nieswandt B. STIM and Orai in hemostasis 3. and thrombosis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jun 1;16:2144-60.
50. Varga-Szabo D, Braun A, Nieswandt B. STIM and Orai in platelet function. Cell Calcium. 2011 Sep;50(3):270-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2011.04.002.
51. Bender M, Hofmann S, Stegner D, Chalaris A, Bösl M, Braun A, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Nieswandt B. Differentially regulated GPVI ectodomain shedding by multiple platelet-expressed proteinases. Blood. 2010 Oct 28;116(17):3347-55.
52. Gilio K, van Kruchten R, Braun A, Berna-Erro A, Feijge MA, Stegner D, van der Meijden PE, Kuijpers MJ, Varga-Szabo D, Heemskerk JW, Nieswandt B. Roles of platelet STIM1 and Orai1 in glycoprotein VI- and thrombin-dependent procoagulant activity and thrombus formation. J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 30;285(31):23629-38.
53. Elvers M, Stegner D, Hagedorn I, Kleinschnitz C, Braun A, Kuijpers ME, Boesl M, Chen Q, Heemskerk JW, Stoll G, Frohman MA, Nieswandt B. Impaired alpha(IIb)beta(3) integrin activation and shear-dependent thrombus formation in mice lacking phospholipase D1. Sci Signal. 2010 Jan 5;3(103):ra1.
54. Schuhmann MK, Stegner D, Berna-Erro A, Bittner S, Braun A, Kleinschnitz C, Stoll G, Wiendl H, Meuth SG, Nieswandt B. Stromal interaction molecules 1 and 2 are key regulators of autoreactive T cell activation in murine autoimmune central nervous system inflammation. J Immunol. 2010 Feb 1;184(3):1536-42
55. Berna-Erro A, Braun A, Kraft R, Kleinschnitz C, Schuhmann MK, Stegner D, Wultsch T, Eilers J, Meuth SG, Stoll G, Nieswandt B. STIM2 regulates capacitive Ca2+ entry in neurons and plays a key role in hypoxic neuronal cell death. Sci Signal. 2009 Oct 20;2(93):ra67.
56. Beyersdorf N, Braun A, Vögtle T, Varga-Szabo D, Galdos RR, Kissler S, Kerkau T, Nieswandt B. STIM1-independent T cell development and effector function in vivo. J Immunol. 2009 Mar 15;182(6):3390-7.
57. Böttcher RT, Wiesner S, Braun A, Wimmer R, Berna A, Elad N, Medalia O, Pfeifer A, Aszódi A, Costell M, Fässler R. Profilin 1 is required for abscission during late cytokinesis of chondrocytes. EMBO J. 2009 Apr 22;28(8):1157-69.
58. Braun A, Gessner JE, Varga-Szabo D, Syed SN, Konrad S, Stegner D, Vögtle T, Schmidt RE, Nieswandt B. STIM1 is essential for Fcgamma receptor activation and autoimmune inflammation. Blood. 2009 Jan 29;113(5):1097-104.
59. Nevalainen EM, Skwarek-Maruszewska A, Braun A, Moser M, Lappalainen P. Two biochemically distinct and tissue-specific twinfilin isoforms are generated from the mouse Twf2 gene by alternative promoter usage. Biochem J. 2009 Jan 15;417(2):593-600.
60. Braun A, Varga-Szabo D, Kleinschnitz C, Pleines I, Bender M, Austinat M, Bösl M, Stoll G, Nieswandt B. Orai1 (CRACM1) is the platelet SOC channel and essential for pathological thrombus formation. Blood. 2009 Feb 26;113(9):2056-63.
61. Varga-Szabo D, Braun A, Kleinschnitz C, Bender M, Pleines I, Pham M, Renné T, Stoll G, Nieswandt B. The calcium sensor STIM1 is an essential mediator of arterial thrombosis and ischemic brain infarction. J Exp Med. 2008 Jul 7;205(7):1583-91.
62. Varga-Szabo D, Authi KS, Braun A, Bender M, Ambily A, Hassock SR, Gudermann T, Dietrich A, Nieswandt B. Store-operated Ca(2+) entry in platelets occurs independently of transient receptor potential (TRP) C1. Pflugers Arch. 2008 Nov;457(2):377-87. 18546016.
63. Fritsch A, Loeckermann S, Kern JS, Braun A, Bösl MR, Bley TA, Schumann H, von Elverfeldt D, Paul D, Erlacher M, Berens von Rautenfeld D, Hausser I, Fässler R, Bruckner-Tuderman L. A hypomorphic mouse model of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa reveals mechanisms of disease and response to fibroblast therapy. J Clin Invest. 2008 May;118(5):1669-79.
64. Suemoto H, Muragaki Y, Nishioka K, Sato M, Ooshima A, Itoh S, Hatamura I, Ozaki M, Braun A, Gustafsson E, Fässler R. Trps1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes through Stat3 signaling. Dev Biol. 2007 Dec 15;312(2):572-81.
65. Grosse J, Braun A, Varga-Szabo D, Beyersdorf N, Schneider B, Zeitlmann L, Hanke P, Schropp P, Mühlstedt S, Zorn C, Huber M, Schmittwolf C, Jagla W, Yu P, Kerkau T, Schulze H, Nehls M, Nieswandt B. An EF hand mutation in Stim1 causes premature platelet activation and bleeding in mice. J Clin Invest. 2007 Nov;117(11):3540-50.
66. Chu H, Thievessen I, Sixt M, Lämmermann T, Waisman A, Braun A, Noegel AA, Fässler R. gamma-Parvin is dispensable for hematopoiesis, leukocyte trafficking, and T-cell-dependent antibody response. Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;26(5):1817-25.
67. Stanchi F, Bordoy R, Kudlacek O, Braun A, Pfeifer A, Moser M, Fässler R. 4. Consequences of loss of PINCH2 expression in mice. J Cell Sci. 2005 Dec 5. 15;118(Pt 24):5899-910. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02686.
68. Li S, Bordoy R, Stanchi F, Moser M, Braun A, Kudlacek O, Wewer UM, Yurchenco PD, Fässler R. PINCH1 regulates cell-matrix and cell-cell adhesions, cell polarity and cell survival during the peri implantation stage. J Cell Sci. 2005 Jul 1;118(Pt 13):2913-21.
69. Sakai T, Li S, Docheva D, Grashoff C, Sakai K, Kostka G, Braun A, Pfeifer A, Yurchenco PD, Fässler R. Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is required for polarizing the epiblast, cell adhesion, and controlling actin accumulation. Genes Dev. 2003 Apr 1;17(7):926-40.
70. Braun A, Bordoy R, Stanchi F, Moser M, Kostka G G, Ehler E, Brandau O, Fässler R. PINCH2 is a new five LIM domain protein, homologous to PINCHand localized to focal adhesions. Exp Cell Res. 2003 Apr 1;284(2):239-50. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(02)00039-3.
71. Samulowitz U, Kuhn A, Brachtendorf G, Nawroth R, Braun A, Bankfalvi A, Böcker W, Vestweber D. Human endomucin: distribution pattern, expression on high endothelial venules, and decoration with the MECA-79 epitope. Am J Pathol. 2002 May;160(5):1669-81.
72. Braun A, Aszódi A, Hellebrand H, Berna A, Fässler R, Brandau O. Genomic organization of profilin-III and evidence for a transcript expressed exclusively in testis. Gene. 2002 Jan 23;283(1-2):219-25.