AG Keyl
Translational Machine Learning
Translational Machine Learning
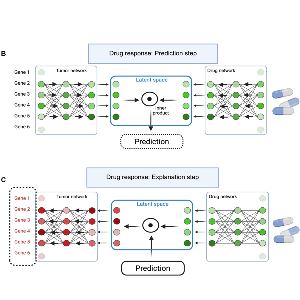
Explainable AI architecture for the prediction of drug response of cancer cells | Keyl et al (2025) | Created with BioRender.com
The complexity of cancer lies far beyond the limits of human intuition. Our goal is to understand this complexity using explainable artificial intelligence (xAI) and translate these findings into actionable clinical insights.
Our translational research is based on a broad spectrum of data modalities, such as proteomics, single-cell RNA seq data, digital histopathology as well as tabular and unstructured (e.g. text) clinical information. The integration of these data requires the application of various machine learning techniques that depend on the specific subtask and comprise robust statistical techniques as well as novel neural network architectures.
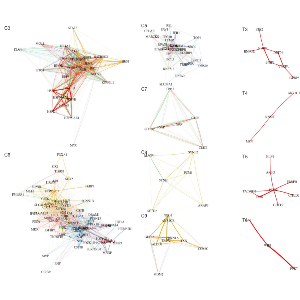
Prediction of gene-regulatory networks (GRN) from scRNA-seq data via explainable AI | Keyl et al. (2023)
By integrating single-cell molecular profiles with clinical outcome data, we aim to identify robust cancer- and immune-cell signatures that stratify patients and predict disease progression and treatment response, ultimately supporting more precise and effective cancer therapies. We develop xAI methods for single-cell RNA sequencing data to dissect regulatory mechanisms at the level of individual cancer cells, providing mechanistic insight beyond predictive performance.
In parallel, we integrate preclinical molecular and pharmacological datasets within unified multimodal models to model how transcriptional cancer profiles determine drug sensitivity and resistance, enabling the systematic identification of candidate target genes and actionable vulnerabilities.
Explainable AI architecture for the prediction of drug response of cancer cells | Keyl et al (2025) | Created with BioRender.com
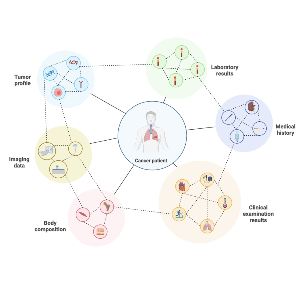
Precision oncology relies on a deep understanding of each patient’s individual characteristics, including their medical history, lab results, and free text information. Using xAI, we analyse this routine clinical information to better support treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes. By applying xAI to model outcomes across large pan-cancer datasets of routine clinical data, we model each patient’s individual disease trajectory and uncover relationships between key patient characteristics and the patient prognosis.In addition, we aim to integrate these clinical models with detailed information from histopathological slides, creating interpretable frameworks that link tumor tissue morphology with clinical data, ultimately supporting treatment decisions and patient-specific predictions.
Doctoral Researcher (PhD)
Doctoral Researcher (MD)
We welcome motivated people to join our research projects at the interface of precision medicine and machine learning. You will work in a research-intensive environment with strong expertise in AI for medical applications and have the chance to collaborate with people from diverse backgrounds across our group and other research teams. Participants will gain hands-on experience with cutting-edge methods, develop their skills, and contribute to innovative, data-driven research.
Bosserhoff, J., Keyl, J., Lenfers, T., Führer-Sakel, D., Wichert, M., Klauschen, F., Schuler, M., Hartmann, S., Keyl, P.*, Kleesiek, J.*, 2025.
Characterizing and Predicting End-of-Life Patient Trajectories Using Routine Clinical Data.
medRxive
Kiermeyer, N.*, Lenfers, T.*, Dada, A., Friedrich, J., Khattab, S., Knop, E., Egger, J., Pauly, M., Jung, A., Montavon, G., Siveke, J.T., Wiesweg, M., Kasper, S., Neumann, U.P., Klauschen, F., Hartmann, S., Schuler, M., Keyl, P.*, Kleesiek, J.*, Keyl, J.*, 2025.
Large Language Models Improve Cancer Survival Prediction Using Real-World Clinical Notes.
medRxive
Keyl, P., Keyl, J., Mock, A., Dernbach, G., Mochmann, L.H., Kiermeyer, N., Jurmeister, P., Bockmayr, M., Schwarz, R.F., Montavon, G., Müller, K.-R., Klauschen, F., 2025.
Neural interaction explainable AI predicts drug response across cancers.
NAR Cancer 7,
Keyl, J.*, Keyl, P.*, Montavon, G., Hosch, R., Brehmer, A., Mochmann, L., Jurmeister, P., Dernbach, G., Kim, M., Koitka, S., Bauer, S., Bechrakis, N., Forsting, M., Führer-Sakel, D., Glas, M., Grünwald, V., Hadaschik, B., Haubold, J., Herrmann, K., Kasper, S., Kimmig, R., Lang, S., Rassaf, T., Roesch, A., Schadendorf, D., Siveke, J.T., Stuschke, M., Sure, U., Totzeck, M., Welt, A., Wiesweg, M., Baba, H.A., Nensa, F., Egger, J., Müller, K.-R., Schuler, M., Klauschen, F., Kleesiek, J., 2025.
Decoding pan-cancer treatment outcomes using multimodal real-world data and explainable artificial intelligence.
Nat. Cancer 6, 307–322. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-024-00891-1
Klauschen, F., Dippel, J., Keyl, P., Jurmeister, P., Bockmayr, M., Mock, A., Buchstab, O., Alber, M., Ruff, L., Montavon, G., Müller, K.-R., 2024.
Toward Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Precision Pathology.
Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 19, 518362039. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-051222-113147
Keyl, P., Bischoff, P., Dernbach, G., Bockmayr, M., Fritz, R., Horst, D., Blüthgen, N., Montavon, G., Müller, K.-R., Klauschen, F., 2023.
Single-cell gene regulatory network prediction by explainable AI.
Nucleic Acids Res. 51, e20–e20. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1212
Keyl, P.*, Bockmayr, M.*, Heim, D., Dernbach, G., Montavon, G., Müller, K.-R., Klauschen, F., 2022.
Patient-level proteomic network prediction by explainable artificial intelligence.
Npj Precis. Oncol. 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-022-00278-4